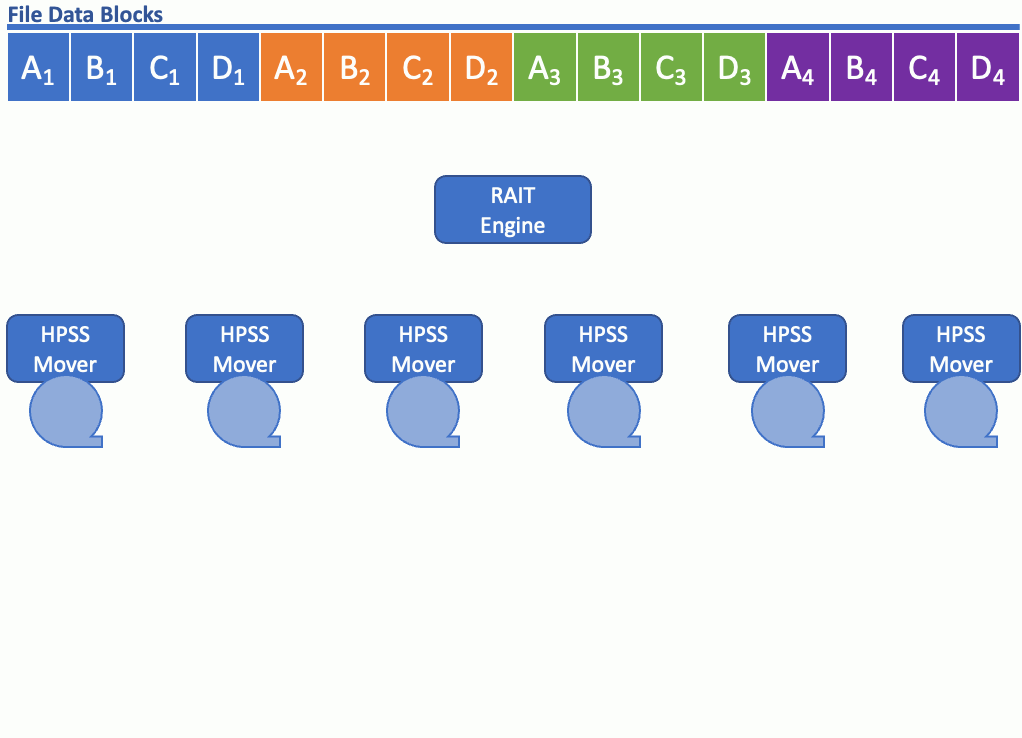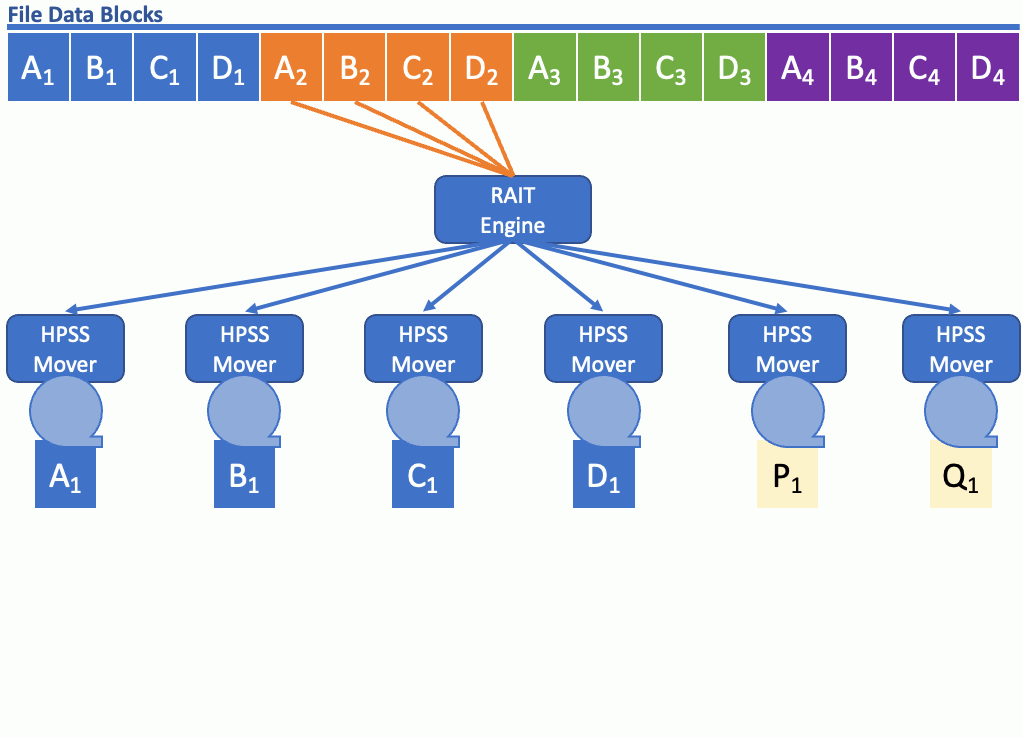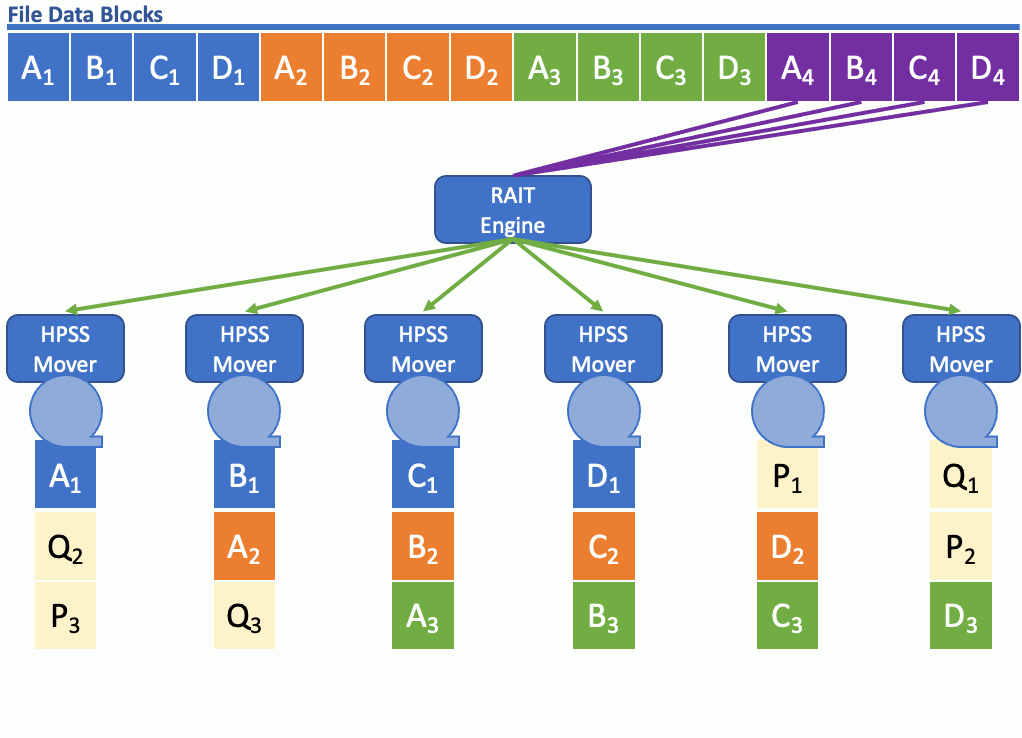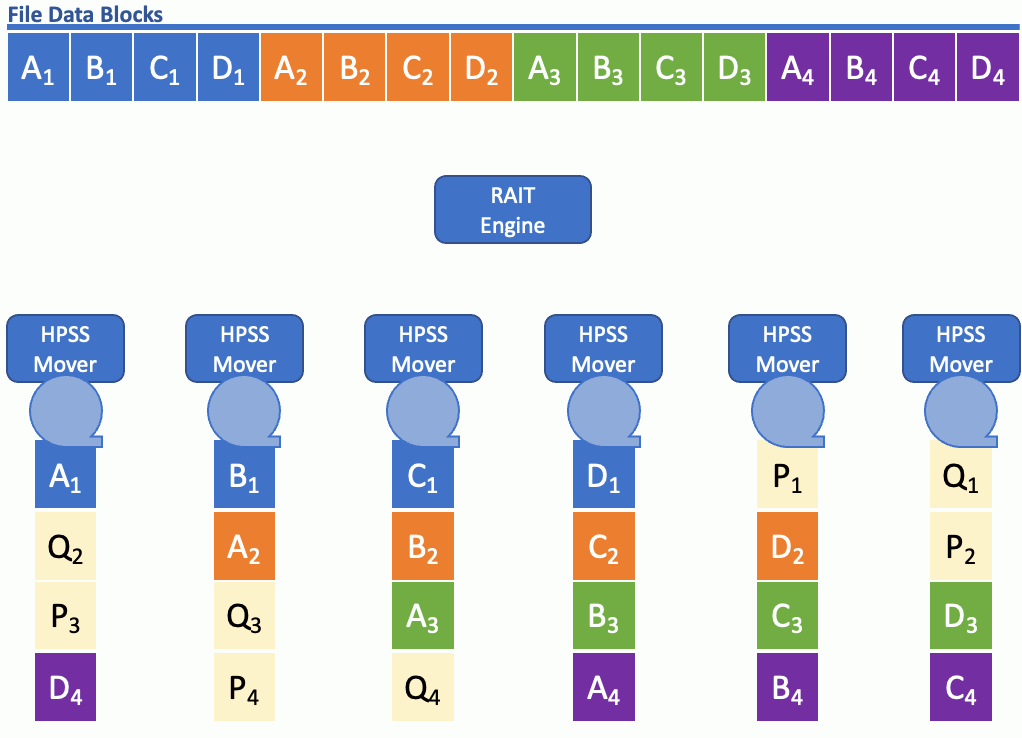
WHAT IS HPSS RAIT?
HPSS RAIT (Redundant Array of Independent Tapes) is an HPSS software technology for striping data on tape with the added benefit of parity for redundancy. HPSS RAIT with single parity is similar to RAID-5 and HPSS RAIT with two parities is similar to RAID-6, except HPSS RAIT is used with tape. HPSS with RAIT still streams the tape drives at hardware speed, and stripe widths of up to 16 (data+parity) are available.
HPSS RAIT is transparent to the client using any of the existing HPSS client interfaces: HPSSFS Fuse, SwiftOnHPSS, FTP, Parallel FTP, HSI, HTAR, and other third-party HPSS client applications.
WHY USE HPSS RAIT?
RAIT allows data to flow to and from tape in a parallel manner
Parallel tape I/O allows single file transfers to exceed the native transfer rate of a single tape drive. At one DOE site, large file I/O exceeded 1 GB/s with their 4+P HPSS RAIT stripe deployed on 250 MB/s tape technology. Thus, a 1 TB file can be written to tape in less than 17 minutes. Without parallel I/O, a 1 TB file might take over an hour to transfer using a single 250 MB/s tape drive.
When compared to dual-copy tape, HPSS RAIT lowers redundant tape costs.
At the lowest level, a 2+P HPSS RAIT will deliver up to 2x improvement in tape bandwidth and typically cuts the cost of redundant tape by 45%. Redundant tape costs are cut by 45%, rather than 50%, because typically 90% of the files by count only take 10% of the space in an HPSS repository, while 10% of the files by count take up 90% of the space. HPSS RAIT is intended for large files, so for greater recall efficiency, dual-copy tape is used to protect smaller files.
There are two basic methods of redundancy: making multiple copies (mirroring), and redundancy through error-correcting codes (such as Reed-Solomon). RAIT uses Reed-Solomon error-correcting codes which are less expensive than making multiple copies due to the lower tape, drive, space, and power requirements.
THE VALUE OF RAIT OVER MIRRORING
Use Less Media
There is a lower cost of fault tolerance with RAIT: fewer tape drives and cartridges are required. There are also faster mount times when compared with writing to a mirrored volume. For example, in the case of an 8 tape stripe and adding single failure tape, resulting in a total of 9 tapes to accomplish the redundancy.
Automatic Data Recovery
There is a high tolerance for tape loss within the HPSS RAIT stripe. RAIT reads and RAIT writes will continue even if there is a tape mount or tape media error. Automatic data recovery takes place during the RAIT read operation because HPSS can reconstruct the missing data using the parity and surviving data blocks.